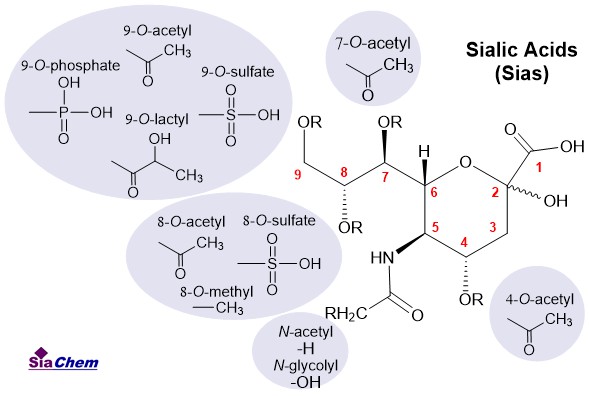
Sialic acids (Sias) are a family of nine-carbon sugar neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-D-galactononulsonic acid) derivatives. Sialic acids are abundant in the animal kingdom and are found in different forms. Their most common form is N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac). The N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) is another commonly found sialic acid in animals that cannot be synthesized in humans due to a gene defect. However, human beings can acquire Neu5Gc through their diet [1]. Additional chemical modifications of Neu5Ac are its four hydroxyl groups (at C-4, 7, 8, and 9 position), including O-acetylation, O-sulfation, O-methylation, O-lactylation, or O-phosphorylation. In total, over 50 different naturally-occurring sialic acids have been identified so far [2-5].