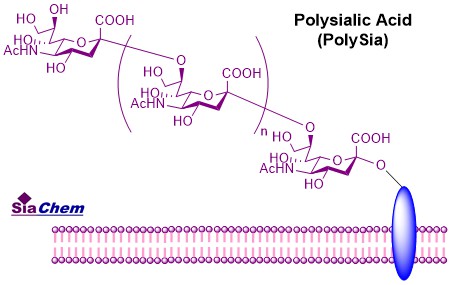
Polysialic acid (polySia), a homopolymer of α2,8-linked sialic acid, is one of the polysaccharide expressed on neural precursors in the embryonic and adult brain [1]. Polysialic acid, synthesized by two polysialyltransferases (ST8SiaII and ST8SiaIV) [2]. The main carrier of polySia in eukaryotes is the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), whose adhesion properties polySia modulates. PolySia has a pivotal role during normal neural development in cell motility and synaptic plasticity, while in the adult cerebrum polySia is involved in spatial learning and memory [1]. PolySia also serves as an oncofetal antigen in several cancers of neuroectodermal origin [3, 4]. PolySia also functions as an antiadhesive by virtue of its large polyanionic charge, thereby negatively regulating cell–cell interaction, and is implicated in cell migration [5,6].